Introduction
SymbolicAI: A Neuro-Symbolic Perspective on Large Language Models (LLMs)
Overview
SymbolicAI is a framework that leverages machine learning, specifically Large Language Models (LLMs), as its foundation and composes operations based on task-specific prompting. Our approach adopts a divide-and-conquer strategy to break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable tasks. By reassembling these operations, we can solve intricate problems efficiently.
Read full paper here.
Key Features
Seamless transition between differentiable and classical programming
Neuro-symbolic computation using LLMs
Composable operations for complex problem-solving
Integration with various engines (OpenAI, WolframAlpha, OCR, etc.)
Support for multimodal inputs and outputs
🤷♂️ Why SymbolicAI?
SymbolicAI aims to bridge the gap between classical programming (Software 1.0) and modern data-driven programming (Software 2.0). It enables the creation of software applications that harness the power of large language models while maintaining the benefits of composability and inheritance from object-oriented programming.
By using SymbolicAI, you can traverse the spectrum between the classical programming realm and the data-driven programming realm, as illustrated in the following figure:
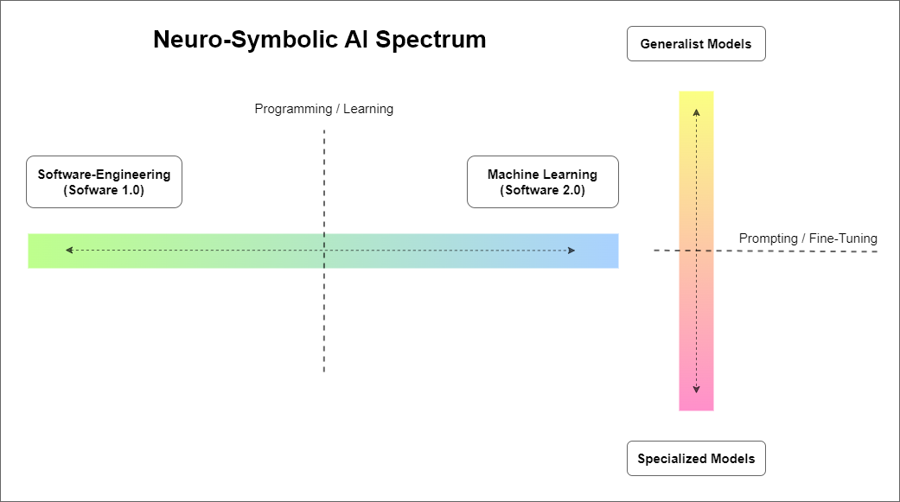
We adopt a divide-and-conquer approach, breaking down complex problems into smaller, manageable tasks. We use the expressiveness and flexibility of LLMs to evaluate these sub-problems. By re-combining the results of these operations, we can solve the broader, more complex problem.
In time, and with sufficient data, we can gradually transition from general-purpose LLMs with zero and few-shot learning capabilities to specialized, fine-tuned models designed to solve specific problems. This strategy enables the design of operations with fine-tuned, task-specific behavior.
Core Concepts
Symbols: All data objects are treated as symbols, with natural language as the primary interface for interaction.
Operations: Contextualized functions that manipulate symbols and return new objects.
Expressions: Non-terminal symbols that can be further evaluated, allowing for complex computational graphs.
Engines: Various backends (e.g., GPT-3, WolframAlpha, CLIP) that power different types of computations and transformations.
 More fun facts!
More fun facts!
 More fun facts!
More fun facts!SymbolicAI is fundamentally inspired by the neuro-symbolic programming paradigm.
Neuro-symbolic programming is an artificial intelligence and cognitive computing paradigm that combines the strengths of deep neural networks and symbolic reasoning.
Deep neural networks are machine learning algorithms inspired by the structure and function of biological neural networks. They excel in tasks such as image recognition and natural language processing. However, they struggle with tasks that necessitate explicit reasoning, like long-term planning, problem-solving, and understanding causal relationships.
Symbolic reasoning uses formal languages and logical rules to represent knowledge, enabling tasks such as planning, problem-solving, and understanding causal relationships. While symbolic reasoning systems excel in tasks requiring explicit reasoning, they fall short in tasks demanding pattern recognition or generalization, like image recognition or natural language processing.
Neuro-symbolic programming aims to merge the strengths of both neural networks and symbolic reasoning, creating AI systems capable of handling various tasks. This combination is achieved by using neural networks to extract information from data and utilizing symbolic reasoning to make inferences and decisions based on that data. Another approach is for symbolic reasoning to guide the neural networks' generative process and increase interpretability.
Embedded accelerators for LLMs will likely be ubiquitous in future computation platforms, including wearables, smartphones, tablets, and notebooks. These devices will incorporate models similar to GPT-3, ChatGPT, OPT, or Bloom.
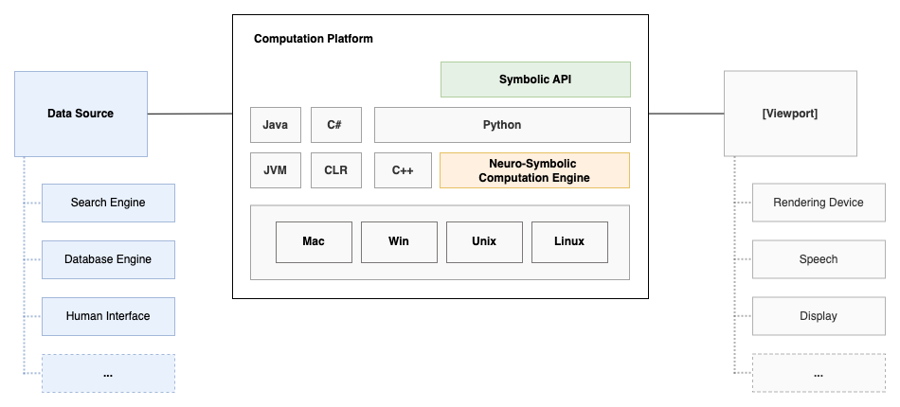
LLMs are expected to perform a wide range of computations, like natural language understanding and decision-making. Additionally, neuro-symbolic computation engines will learn how to tackle unseen tasks and resolve complex problems by querying various data sources for solutions and executing logical statements on top. To ensure the content generated aligns with our objectives, it is crucial to develop methods for instructing, steering, and controlling the generative processes of machine learning models. As a result, our approach works to enable active and transparent flow control of these generative processes.
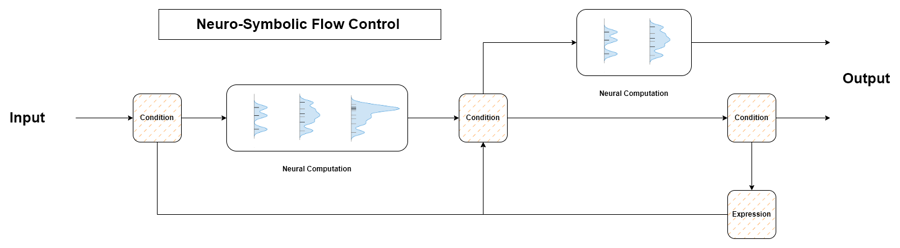
The figure above depicts this generative process as shifting the probability mass of an input stream toward an output stream in a contextualized manner. With properly designed conditions and expressions, you can validate and guide the behavior towards a desired outcome or repeat expressions that fail to meet requirements. Our approach consists of defining a set of fuzzy operations to manipulate the data stream and condition LLMs to align with our goals. We regard all data objects – such as strings, letters, integers, and arrays – as symbols and view natural language as the primary interface for interaction. See the following figure:
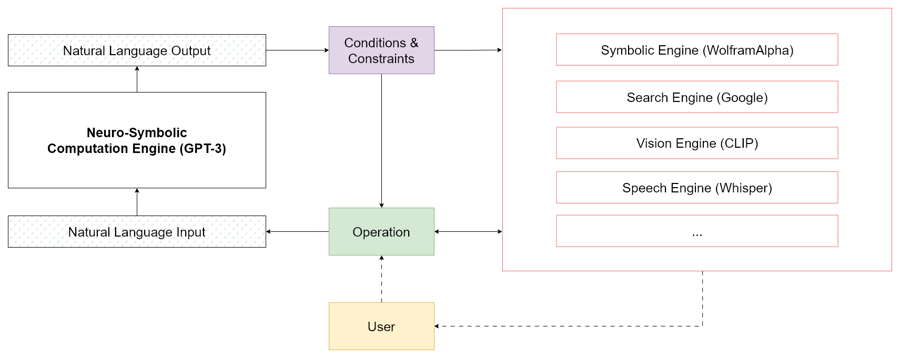
As long as our goals can be expressed through natural language, LLMs can be used for neuro-symbolic computations. Consequently, we develop operations that manipulate these symbols to construct new symbols. Each symbol can be interpreted as a statement, and multiple statements can be combined to formulate a logical expression.
By combining statements together, we can build causal relationship functions and complete computations, transcending reliance purely on inductive approaches. The resulting computational stack resembles a neuro-symbolic computation engine at its core, facilitating the creation of new applications in tandem with established frameworks.
Future Directions
Meta-learning semantic concepts on top of neuro-symbolic expressions
Self-evolving and self-healing API
Integration with reinforcement learning
Advancement in prompt design and value alignment methods
SymbolicAI opens up new possibilities for creating applications that can perform self-analysis and self-repair, pushing the boundaries of what's possible with LLMs and neuro-symbolic computation.
Last updated